Business Process Optimization (BPO)
Business Process Optimization - BPO
Without doubt the main characteristic of a good project manager is to create a culture of continuous improvement and process optimization and improve the existing business workflows.
Over the last 20 years we have seen many improvements in regards to project management. We have the introduction of project management methodologies such as Agile, Lean and Six Sigma.
What optimization mean?
Optimization is an act, process or methodology of making something (such as design, system or decision) as fully perfect, functional or effective as possible. An everyday example of optimization could be a Solutions Lead planning to discuss with internal or external customers. The Solutions Lead, before proceeding to the final solution, he/she could propose existing solutions or even research of expanding the existing solutions to the customers. In other words, the Solutions Lead is making the most of his/her and team's time. Also, companies expenses are reduced as additional analysis, research and development are reduced.
Why optimize processes?
The main goal of process optimization is to reduce or eliminate time and resource wastage, unnecessary costs, bottlenecks, and mistakes while achieving the process objective. It is almost impossible to manage a multiple process without optimization. Optimization is so important because it is actually the only way to track the business processes. It assures the each one is performing at its full ability.
Process optimization is also an integral part of Agile project management. The software development process requires an stable and constant approach, where steps are repeated and consistent. One example could be a telecommunications Software product development team that regularly deploys bug fixes. This ensures that the software product is fully ready before it is launched.
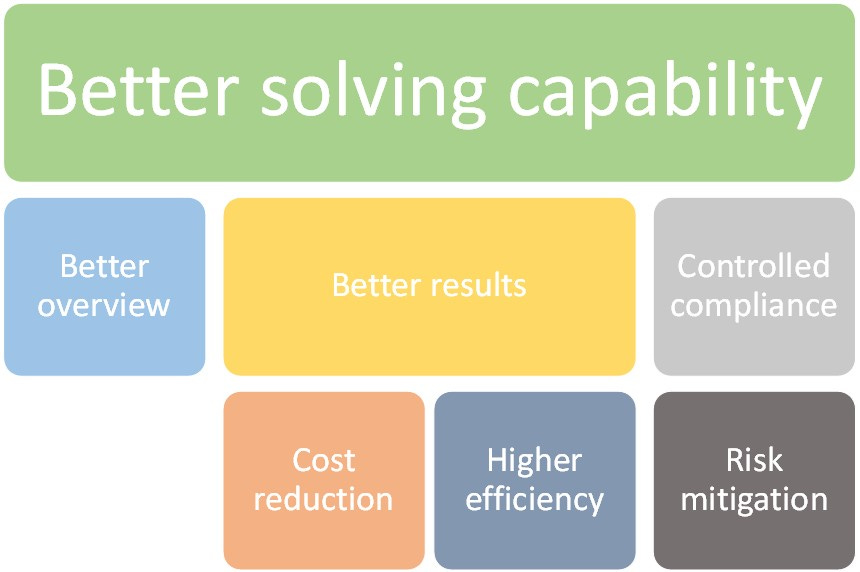
When you optimize project management processes, you're increasing the likelihood of a host of benefits. These include:
Better overview
You get a clear general view over all processes, which helps integration and optimization of the business as a whole.
Better problem-solving capability
With an end-to-end view, you can find the causes of problems. This aids to fix mistakes at their source, so managers don’t need to invest resources in mitigating consequences instead of actually resolving issues.
Better results
Improved internal and external processes are one of the greatest benefits, since the chances are improved of delivering the quality that customers seek in a product or service provider. This is a way to achieve an outstanding market position and offer greater value.
Controlled compliance
It’s easier to stay compliant with standardized and monitored processes. Plus, in the event of an audit, transparency in processes eases the proceedings and contributes to the desired results.
Cost reduction
When processes are optimized, waste can be easily identified, which makes it possible to find errors, poorly used resources, bottlenecks that compromise productivity, and so on. This in turn helps resolve these issues and reduce expenses.
Higher efficiency
Business process optimization allows products and services to be delivered with agility and quality, because with mistakes corrected and processes standardized, you can produce more in less time, and with more quality.
Optimized time management
Tasks that don’t add value can be eliminated without any impact. This maximizes time and creates more agile workflows.
Risk mitigation
Mapping activities makes it easier to standardize processes and formalize them. This reduces errors, repetition, and questions regarding procedures, which as a result reduces risks.
Based on these benefits, make sure you always pay attention to symptoms of poor process management in your company and try to "heal" them.
What are the challenges of process optimizations?
There are plenty of hurdles to process optimization.
One major obstacle is that it can require intensive resources. The main process optimization techniques have many steps that need to be implemented, requiring data analysis, time and effort. However, one of the overall goals of process optimization is to make the most of project resources. Therefore, it could be argued that if team members give some effort to optimizing processes initially, they will save a lot more time in the long run.
Another challenge with process optimization is that some team members may be resistant to change. It can be difficult to convince people to alter their daily practices, especially if there are no apparent disadvantages to them. In addition to employee pushback, there will also be a starting period where people adapt to the new way of doing things. The key here is for project managers to share their vision with the team early, highlighting the multiple advantages of process optimization to get everyone on board.
Finally, there's another risk to be wary of: optimizing processes for optimization’s sake. While it is important to identify areas for improvement and go all out for new achievements, the potential disruption caused by an ill-conceived process optimization plan can be highly harmful to a business. Project managers should conduct extensive research before implementing any kind of process optimization and be confident that there is strong potential for an improved outcome.
Process optimization methods and techniques
There are many process optimization techniques you can use to get you started. Here are three examples:
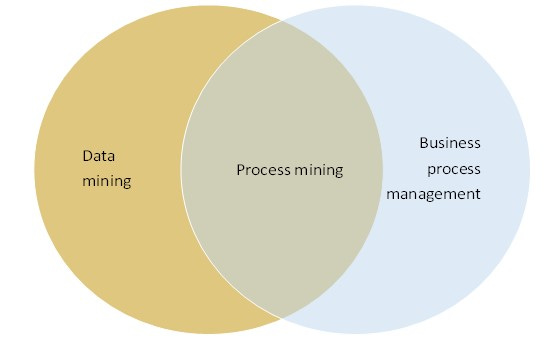
Process mining:
Process mining is a family of techniques relating the fields of data science and process management to support the analysis of operational processes based on event logs. The goal of process mining is to turn event data into insights and actions. ... Process mining starts from event data.
DMAIC: DMAIC is a data-focused method used in Six Sigma to improve processes. It stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. These five stages combine to form a cycle. First, customers are defined. Then, performance is measured, and the data is analyzed. Finally, improvements are implemented and controlled to ensure the process remains in optimal condition.
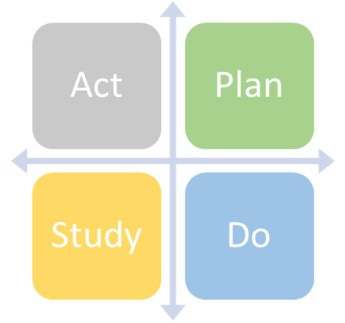
PDSA: The Plan, Do, Study, Act (PDSA) cycle is a method for rapidly testing a change - by planning it, trying it, observing the results, and acting on what is learned. This is a scientific method used for action-oriented learning. After changes are thoroughly tested, PDSA cycles can be used to implement or spread change. The key principle behind the PDSA cycle is to test on a small scale and test quickly.
It's good practice for a project manager to take some time to research various process optimization methods before deciding which one is most suited to their business.
Who should be responsible of process optimization?
A project manager is responsible for initiating process optimization. It is their job to define project processes before making a roadmap of what needs to be optimized. They will then put their plan in action and monitor it to ensure it achieves its goals.
However, to ensure the best plan for process optimization, a project manager needs to consult critical stakeholders to help them in their decision-making. These stakeholders could include the chief operations officer, line manager, business analysts or other senior executives. This is to ensure that the process optimization plan will be suitable for the relevant department.
If you’re finding this newsletter valuable, consider sharing it with friends, or subscribing if you haven’t already.
Sincerely,
Stathis 👋